Dosinia lupinus (Linnaeus, 1758)
Smooth Dosinia| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
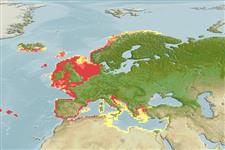
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Dosinia lupinus AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Classification / Names आम नाम | उपशब्द | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Venerida | Veneridae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / गहराई सीमा / distribution range पारिस्थितिकी
; गहराई सीमा 0 - 125 m (संदर्भ 2736). Subtropical
Distribution देश | ऐफ ऐ ओ क्षेत्र | Ecosystems | संयोग | भूमिका
Northeast Atlantic and the Mediterranean.
Length at first maturity / आकार / Weight / Age
परिपक्व अवधि: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 3.1 cm SHL पुल्लिंग / अलिंग; (संदर्भ 2758)
Life cycle and mating behavior परिपक्व अवधि | पुनरुत्पत्ति | मछलीऔ का अंडे देना | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Main reference
संदर्भ | संयोजक | सहयोगीयो
Gaspar, M.B., M.N. Santos, P. Vasconcelos and C.C. Monteiro 2002 Shell mophometric relationships of the most common bivalve species (Mollusca: Bivalvia) of the Algarve coast (southern Portugal). Hydrobiologia 477:73-80. (संदर्भ 2736)
IUCN Red List Status
(संदर्भ 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (संदर्भ 108899)
CMS (संदर्भ 116361)
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
साधन
अधिक जानकारी
संघटक आहार
आहार खपत
परभक्षी
इंटरनेट स्रोत
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, खोज) | Zoological Record



