Common names from other countries
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
Récifal; profondeur 1 - 15 m (Ref. 113378). Tropical
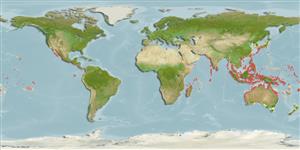
Indo-Pacific: Mozambique to Japan, Australia and Papua New Guinea.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Description synthétique
Morphologie
Body is transparent with large white spots. Four to five orange spots with a black ring are present on the tail fan. Purplish-blue rings are present near the joints and tips of pereiopods. Rostrum well-developed, with five to six dorsal, and two ventral teeth. Females are generally larger.
Minimum depth from Ref. 83472. Epizoic, Intertidal to subtidal (Ref. 106854). Associated with giant anemones (Ref. 113378). Usually found in pairs. Occasionally found on hard corals (Ref. 125532).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturité | Reproduction | Frai | Œufs | Fécondité | Larves
Members of the order Decapoda are mostly gonochoric. Mating behavior: Precopulatory courtship ritual is common (through olfactory and tactile cues); usually indirect sperm transfer.
Bruce, A.J. 2005. (Ref. 83471)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
statut CITES (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Utilisations par l'homme
| FishSource |
Outils
Plus d'informations
Taille/ÂgeCroissanceLongueur-poidsLongueur-longueurMorphologieLarvesAbondance
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref.
115969): 22.9 - 29.3, mean 28.3 (based on 3320 cells).